
Aymen Ghorbal
This article has been reviewed by Aymen Ghorbal, Executive VP and Global Business Development. Contact Us and our application engineers will assist you with your application.
Scotch yoke actuators are 90˚ driving mechanisms that can be powered by compressed air or hydraulic oil from an external source. This mechanical actuator is designed to automate the operation of quarter-turn valves (rotary valves), such as ball and butterfly valves, by converting linear motion into rotary motion. In industrial automation, controlling valve motion efficiently is critical for performance and durability. The scotch yoke mechanism is a widely used mechanism in heavy-duty applications, particularly in industries requiring high torque at the start and end of a stroke.

Its unique Scotch Yoke mechanism allows for higher torque at the start and end of the stroke, making it ideal for applications where overcoming initial resistance is critical. These actuators are designed to automate quarter-turn valves, providing smooth operation while meeting strict torque requirements. Their compact design and ability to withstand high temperature environments make them ideal for demanding applications like oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation.
How do they work?
A scotch yoke actuator typically consists of a crank and piston system in a hollow cylinder. Pressure is applied to a side of the piston inside the cylinder. As a result, force is generated which moves the piston along the axis of the cylinder to rotate the actuator stem 90° with pilot air application. When the pressure is relieved, the piston then returns to its original position by a spring.
A pneumatic actuator uses air pressure to drive the piston rod, which in turn engages the scotch yoke mechanism. This system can be double acting, where air is applied to both sides of the piston rod for precise bidirectional motion, or spring-return, where a spring module ensures return motion when air is released. The spring module acts as a damper, preventing excessive acceleration during operation and reducing stress on internal components.
Scotch Yoke Mechanisim Explained
The Scotch Yoke mechanism is a mechanical system that converts rotational motion into linear motion or vice versa. It consists of a sliding yoke with a slot, a crank or pin, a piston rod, and a fixed link. As the crank rotates, the attached pin moves within the slot of the yoke, forcing the yoke to move linearly. This design provides a smooth sinusoidal motion with high torque output at specific points in the cycle.
Key Components
- Crank (or Pin): Rotates to drive the mechanism.
- Yoke (Sliding Block): Contains a slot that guides the pin’s movement, resulting in linear displacement.
- Piston Rod: Connects the yoke to the piston, transferring linear motion for applications such as engine pistons, actuators, or compressors.
- Fixed Link: Serves as the pivot point for the crank’s rotation.
Modular Design Benefits
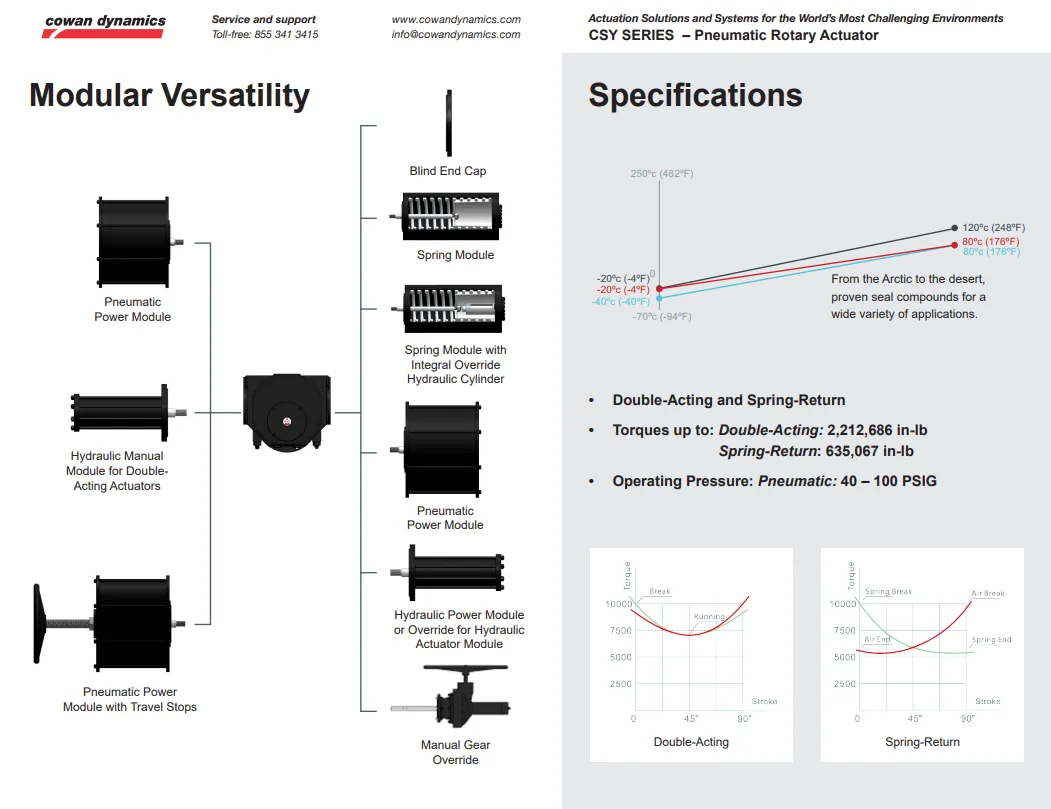
For example, the CSY Series Scotch Yoke Actuator by Cowan Dynamics boasts a modular design that offers significant advantages in industrial applications. This modularity allows for the seamless integration of various components, enabling customization to meet specific operational requirements.
For instance, the actuator can be configured as either double-acting or spring-return, depending on the desired motion control. Additionally, modules such as hydraulic manual overrides and pneumatic power units can be incorporated without altering the actuator’s overall dimensions, providing flexibility and adaptability in diverse industrial settings.
This approach not only enhances the actuator’s reliability but also allows for future upgrades or modifications with minimal disruption to existing systems. By adopting a modular architecture, the CSY Series ensures that industries can maintain efficient operations while easily adapting to evolving technological demands.
Why consider a Scotch yoke valve actuator?
Deciding which actuator is best for a certain application depends on several factors like environment, required accuracy, and close/open speed. A scotch yoke valve actuator is engineered to automate all types of quarter-turn valves (butterfly, ball, plug, and damper) with various torque profiles to provide a “best fit” for every application.
When choosing between a 90˚ actuator such as a Rack & Pinion or Scotch Yoke, the main difference between these actuators are the torques they can generate.
The following table shows the difference between a scotch yoke actuator and rack and pinion.
| Parameter | Scotch Yoke | Rack & Pinion | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Torque | High at the beginning and end of movement | Lower, but constant | Scotch yoke delivers peak torque at stroke ends, useful for overcoming valve seating forces. |
| Lifetime | Long | Long | Both have high cycle life, often exceeding a million cycles. |
| Size | Longer | Relatively shorter | Rack & pinion actuators are more compact, saving space. |
| Cost | Medium | Low | Scotch yoke is slightly more expensive due to its mechanism. |
| Torque along the stroke | Nonlinear | Constant | Nonlinear torque makes Scotch yoke ideal for specific applications. |
| Efficiency | High | Moderate | Fewer moving parts in Scotch yoke reduce energy losses. |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter | Rack & pinion actuators are generally more lightweight. |
| Durability in Harsh Environments | High | Moderate | Scotch yoke is more robust for heavy-duty applications. |
| Maintenance Requirements | Low | Moderate | Fewer wear points in Scotch yoke lead to lower maintenance. |
| Response Time | Moderate | Fast | Rack & pinion responds quickly due to direct motion conversion. |
| Applications | Butterfly valves, ball valves, high-torque applications | General valve automation, quarter-turn valves | Scotch yoke is ideal for applications needing high breakaway torque. |
| Suitable for continuous control (throttling application) | Yes | Yes | Constant torque in rack & pinion makes it suitable for precise control. |
| Preferred Industries | Oil & gas, power plants, heavy-duty industries | Water treatment, HVAC, food processing | Industry preference depends on torque and space requirements. |
Hydraulic vs. Pneumatic Scotch Yoke Actuators
- Pneumatic Scotch Yoke Actuators use compressed air to generate torque, making them ideal for applications requiring fast actuation, lightweight operation, and clean energy sources.
- Hydraulic Scotch Yoke Actuators use pressurized fluid, providing higher force output, making them suitable for high-pressure and heavy-duty applications where air pressure alone is insufficient
What valve types does a scotch yoke actuator work with?
A Scotch Yoke actuator is specifically designed to operate quarter-turn (90° rotation) valves, making it an essential choice for industries requiring efficient and powerful torque delivery. These actuators are particularly well-suited for butterfly valves, ball valves, and plug valves, as well as dampers and other rotary motion applications.
- Butterfly Valves – Common in pipelines, water treatment, and chemical processing due to their lightweight and compact design.
- Ball Valves – Used in oil and gas, petrochemical, and power plants due to their superior sealing capabilities.
- Plug Valves – Common in applications involving viscous fluids, slurries, and abrasive media.
Torque required to operate a valve
The operating torque of a valve is not constant along the stroke. A valve usually requires a higher torque on the start and the end of its stroke.
For a butterfly valve to start opening from a completely closed position, higher torque is required to overcome the friction between the seat and valve body. Lower torques are needed to keep the valve moving in the middle section of the valve stroke.
The torque output of a scotch-yoke actuator changes as a function of stroke position, resulting in higher torque at the beginning and end of the stroke (fig 4).
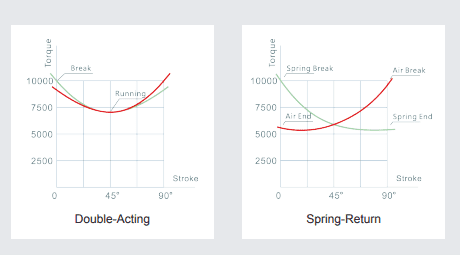
(fig4)
How to select a scotch yoke actuator and size it for a certain valve?
Selection and sizing of a scotch yoke actuator depends on two main values of torque, the following table shows torque values are needed:
|
Torque |
Definition |
|
Start – end |
Torque required to start opening a completely closed valve and to close a completely open valve. |
|
Running torque |
Torque required to keep valve moving between closed and opened positions at a constant velocity. |
Note that valves of the same type, identical Part Number and size can have different torque values due to sealing type and materials.
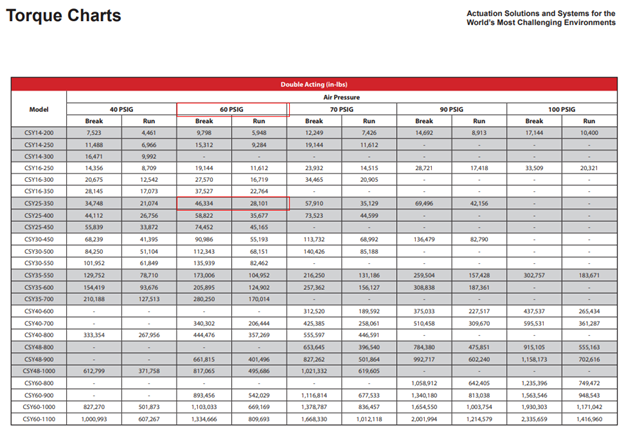
For example, if we have a valve with 44,000 inch-Lbs of start-end torque and 25,000 inch-Lbs running torque, a typical scotch-yoke product selection manual would have a torque rating with required pressure tables as shown below.
When reviewing the table, a min available plant air pressure of 60 psi-g would require an actuator such as the CSY25-350. Now we know which model is fit for the valve and pressure required to operate the actuator.
Scotch & Yoke Pneumatic Actuator – Cowan Series CSY, complete with controls
How to calculate the required volume of air to stroke an actuator?
Now that we have sized the actuator, we need to determine the amount of air that is needed to drive the valve for one full stroke. Stroke volumes are shown in the table below (fig6).
Based on the selected model number, we know that we have a “CSY” a “25” module size and a “350” cylinder size. With this information we can determine the volume of air displaced by the actuator:
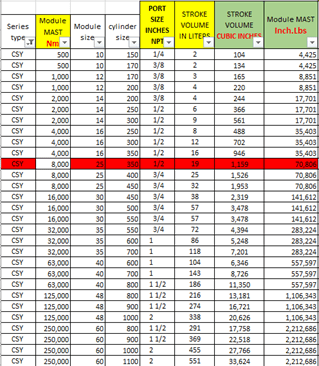
(fig6)
- -air volume closed = 1,159 in3
- -inlet size= ½””
- Therefore, the max volume of air needed to move the actuator a full stroke = air volume closed = 1,159 in3
With the volume of air required to stroke the valve and the needed time to stroke the valve, we can later calculate the required flow coefficient for the accessories and the air consumption.
Applications for a scotch-yoke valve actuator in the industry
- Oil & Gas: actuate valves for isolating flow in pipes
- Mining: actuate valves for isolating nozzles in rocks washing lines
- Water and wastewater: actuate valves for isolating feed lines, filters and tanks
Internal parts and common malfunctions
Usually, malfunctions in scotch-yoke actuators occur due to two main problems:
- Loss of power due to pressure loss
- Wear due to lack of lubrication
- Contamination in the air supply system
Engineered for Demanding Applications
At Cowan Dynamics, our CSY Series are meticulously engineered to meet these exacting standards. We invite you to explore how our CSY Series actuators can be tailored to your specific requirements. For detailed specifications and to discuss how our solutions can enhance your operations, please visit our CSY Series product page or contact our team directly.



